Table of Contents
In today’s rapidly evolving business environment, measuring product success has become a critical factor in determining the viability and profitability of a company. Evaluating the performance and impact of products is essential to make informed decisions, driving strategic objectives, and sustaining a competitive edge.
The measurement of product success goes beyond simple financial metrics. While financial indicators like revenue and profitability are important, they only provide a partial picture of a product’s overall performance. Organizations need a holistic framework that considers various perspectives and key performance indicators (KPIs) to gain a comprehensive understanding.
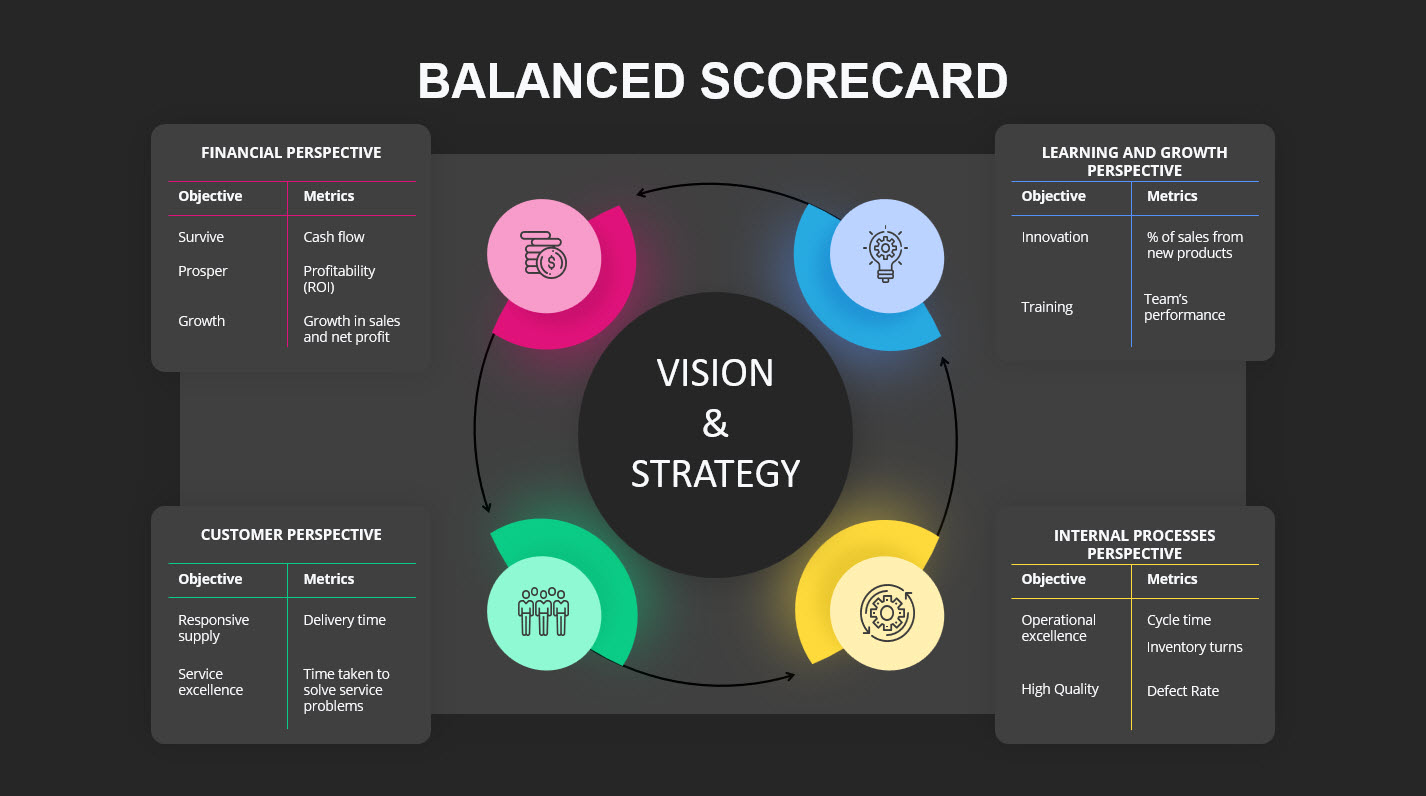
This is where the Balanced Scorecard Framework comes into play. Developed by Drs. Robert Kaplan and David Norton and first described in the Harvard Business Review article back in 1992, the Balanced Scorecard offers a multidimensional approach to measuring and managing product success. It goes beyond financial metrics and takes into account four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth.
By incorporating these perspectives, the Balanced Scorecard Framework ensures a balanced assessment of a product’s performance. It helps organizations align their strategic objectives with measurable KPIs and provides a structured methodology to monitor progress and drive improvement.
What is the Balanced Scorecard Framework
The Balanced Scorecard Framework is a strategic performance measurement and management system that provides organizations with a comprehensive view of their objectives and progress.
The concept behind the Balanced Scorecard Framework emerged as a response to the limitations of traditional financial metrics in capturing the full scope of organizational performance. The framework recognizes that financial measures alone are insufficient for assessing the long-term success and sustainability of an organization.
The Balanced Scorecard Framework incorporates four key perspectives that collectively provide a balanced and holistic view of an organization’s performance:
- Financial Perspective: This perspective examines financial metrics such as revenue, profitability, return on investment, and cash flow. It focuses on the organization’s ability to generate value for shareholders and ensures the financial sustainability of the business.
- Customer Perspective: The customer perspective emphasizes understanding and meeting customer needs. It involves measuring factors like customer satisfaction, loyalty, market share, and customer retention rates. By aligning with customer expectations, organizations can create value and establish a competitive advantage.
- Internal Processes Perspective: This perspective evaluates the efficiency and effectiveness of an organization’s internal operations and processes. It focuses on key areas such as product development, operational efficiency, quality management, and supply chain management. By improving internal processes, organizations can enhance overall performance and customer satisfaction.
- Learning and Growth Perspective: The learning and growth perspective recognizes the importance of developing and nurturing an organization’s human capital and infrastructure. It involves measuring factors such as employee skills, training and development, innovation, and knowledge management. This perspective emphasizes the role of continuous learning and improvement to drive organizational success.
The Balanced Scorecard Framework helps organizations align their strategic objectives with performance metrics by providing a structured methodology. It enables organizations to identify the key drivers of success in each perspective, set measurable targets, and track progress. By using the framework, organizations can ensure that their performance metrics are aligned with their overall strategic goals, fostering better decision-making and resource allocation. This alignment allows organizations to focus on the critical areas that drive success and facilitates effective monitoring and improvement of performance in a balanced manner.
Defining Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable metrics that organizations use to assess progress and performance toward their strategic objectives. They play a vital role in measuring product success within the Balanced Scorecard Framework, providing tangible benchmarks for evaluating performance from each perspective.
When selecting KPIs, it is crucial to choose metrics that align with the organization’s strategic objectives and reflect its priorities. The KPIs should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to provide clarity and facilitate effective performance tracking.
Meaningful KPIs should directly link to the organization’s overall goals and capture the desired outcomes in each perspective. They should be actionable and provide actionable insights to drive decision-making and improvement efforts.
It is important to strike a balance between leading and lagging indicators. While lagging indicators reflect past performance, leading indicators provide early signals of future success. A combination of both helps organizations monitor progress and make proactive adjustments.
Regular review and refinement of KPIs are necessary to ensure they remain relevant and aligned with evolving business objectives. By selecting meaningful and measurable KPIs within the Balanced Scorecard Framework, organizations can gain a clear understanding of their product’s success and make data-driven decisions to drive improvement and achieve long-term success.
Financial Perspective
The financial perspective within the Balanced Scorecard Framework focuses on evaluating the economic impact of a product and its contribution to the overall financial performance of the organization. It involves measuring financial metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that provide insights into product success.
To measure product success from a financial perspective, organizations commonly track metrics such as revenue, profitability, return on investment (ROI), and cash flow. These metrics serve as indicators of the product’s financial viability and effectiveness in generating value for the organization.
Tracking revenue involves monitoring the total income generated from the sales of the product over a specific period. It provides an essential measure of the product’s market demand and pricing effectiveness.
Profitability measures, such as gross profit margin and net profit margin, assess the efficiency of the product’s cost structure and pricing strategy. They indicate the profitability of each unit sold and the overall financial health of the product.
Return on Investment (ROI) calculates the financial return generated by the product relative to the investment made. It considers both the financial gains and the costs associated with developing, producing, and marketing the product.
In addition to these core financial metrics, organizations may also consider other indicators, such as cash flow, working capital, and cost of goods sold (COGS), to gain a comprehensive understanding of the product’s financial performance.
To assess the success of a product, organizations should set clear financial goals and targets. These goals should align with the organization’s overall strategic objectives and take into account factors such as market conditions, competitive landscape, and desired financial outcomes.
Financial goals and targets may include specific revenue targets to be achieved, desired profit margins, targeted ROI levels, and cash flow objectives. They provide a quantitative benchmark against which the product’s financial performance can be evaluated.
By regularly tracking and analyzing financial metrics and KPIs, organizations can assess the success of their products from a financial perspective. This enables them to make informed decisions regarding pricing, cost management, investment allocation, and overall product strategy. It also helps in identifying areas for improvement and opportunities for maximizing financial returns.
Customer Perspective
The customer perspective within the Balanced Scorecard Framework is crucial for measuring product success. It focuses on understanding and meeting customer needs and expectations, ultimately driving customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention. Several customer metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are relevant in assessing product success from this perspective.
Customer satisfaction is a fundamental metric that indicates how well a product meets customer expectations. It can be measured through surveys, feedback mechanisms, or customer satisfaction ratings. High satisfaction levels reflect a positive product experience and increase the likelihood of customer loyalty and repeat purchases.
Customer loyalty is another critical indicator of product success. KPIs such as customer retention rates repeat purchase rates, and customer lifetime value help assess the level of loyalty a product generates. Building customer loyalty is essential for sustained success, as loyal customers are more likely to become advocates, refer others, and contribute to positive word-of-mouth.
Market share is an important metric that measures the product’s position within the target market. It indicates the product’s popularity and competitiveness compared to other offerings. Increasing market share demonstrates product success in capturing a larger portion of the market.
Net Promoter Score (NPS) measures customer advocacy and willingness to recommend the product to others. It provides insights into customer perception and helps identify potential areas for improvement.
Understanding customer needs and expectations is vital for product success. By conducting market research, customer surveys, and feedback analysis, organizations can gain valuable insights into what customers truly value in a product. This knowledge helps shape product development, marketing strategies, and customer experience initiatives to align with customer expectations.
The customer perspective emphasizes the importance of providing exceptional customer service. Responsiveness, resolution of issues, and effective communication are critical elements that contribute to customer satisfaction and retention.
By focusing on customer-centric metrics and KPIs, organizations can track the success of their products in meeting customer needs and expectations. This enables them to make informed decisions, enhance the product experience, and build long-term customer relationships. A customer-oriented approach is essential in today’s competitive landscape, where customer loyalty and satisfaction directly impact market share and overall business performance.
Internal Processes Perspective
The internal processes perspective within the Balanced Scorecard Framework focuses on the efficiency and effectiveness of the internal operations that contribute to product success. It involves tracking and improving key process metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) related to product development, production, and delivery.
One of the critical metrics in this perspective is the product development cycle time. It measures the time it takes from ideation to market launch. A shorter development cycle time indicates agility and the ability to respond quickly to market demands, contributing to product success.
Production efficiency metrics such as production cycle time, utilization rates, and defect rates are crucial indicators. These metrics reflect the effectiveness of the manufacturing or production processes and the quality of the final product. Efficient production processes ensure timely delivery of products while maintaining high standards of quality.
Supply chain management metrics are also important, as they impact product success. These metrics may include inventory turnover, supplier performance, and order fulfillment rates. Effective supply chain management ensures a smooth flow of materials and timely delivery of products to customers.
Measuring and improving key internal processes involves analyzing process workflows, identifying bottlenecks, and implementing process optimization strategies. Lean Six Sigma methodologies, process mapping, and continuous improvement practices can be applied to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of internal processes.
Operational efficiency is crucial for product success as it directly affects cost management and customer satisfaction. Streamlining processes, reducing waste, and improving productivity can lead to cost savings, improved resource allocation, and faster time-to-market, contributing to overall product success.
Operational effectiveness also plays a vital role. This involves ensuring that processes are executed with a high level of accuracy, precision, and consistency. It includes adhering to quality standards, regulatory requirements, and customer expectations. Effective internal processes lead to reliable and consistent product outcomes, reinforcing customer trust and satisfaction.
Regular monitoring and measurement of internal process metrics and KPIs allow organizations to identify areas for improvement and take proactive actions. By focusing on optimizing internal processes, organizations can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, improve product quality, and meet customer expectations more effectively, ultimately driving product success.
Learning and Growth Perspective
The learning and growth perspective within the Balanced Scorecard Framework focuses on assessing the capabilities and development of the organization, which directly contributes to product success. It involves tracking specific metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that reflect the organization’s learning, innovation, and adaptability.
Employee satisfaction is a crucial metric in this perspective. Satisfied employees are more likely to be engaged, motivated, and committed to their work, leading to higher productivity and better customer service. Employee satisfaction surveys, retention rates, and feedback mechanisms can be used to assess and improve employee satisfaction levels.
Training effectiveness is another important indicator. It measures the impact of training programs on employee skills, knowledge, and performance. KPIs such as training completion rates, competency assessments, and performance improvement following training can help evaluate the effectiveness of learning initiatives.
Innovation metrics assess the organization’s ability to generate and implement new ideas and solutions. These metrics may include the number of new product/service launches, the percentage of revenue from new offerings, patent filings, and innovation awards. Fostering a culture of innovation and tracking these metrics are essential for sustained product success.
Knowledge management is a critical aspect of the learning and growth perspective. KPIs related to knowledge sharing, communities of practice, and access to information systems can measure the effectiveness of knowledge management practices within the organization. Effective knowledge management ensures that valuable insights and expertise are leveraged for continuous improvement and informed decision-making.
Continuous learning and improvement are paramount in achieving product success. Organizations should promote a learning culture that encourages employees to acquire new skills, stay updated with industry trends, and seek growth opportunities. KPIs related to employee participation in training programs, certification rates, and the implementation of employee suggestions can indicate the organization’s commitment to continuous improvement.
By focusing on learning and growth metrics and KPIs, organizations can build a strong foundation for product success. Continuous learning and development foster innovation, adaptability, and employee engagement. Organizations that invest in their employees’ growth and create an environment conducive to learning are better equipped to meet changing customer needs, drive product innovation, and ultimately achieve long-term success.
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard Framework
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard Framework to measure product success involves several key steps that help align strategic objectives with performance metrics. By following these steps, organizations can effectively measure and track their progress toward achieving product success.
The first step is to set clear and specific objectives. These objectives should be aligned with the organization’s overall strategy and reflect the desired outcomes for the product. Objectives should be measurable, achievable, and relevant to product success.
Once objectives are established, the next step is to identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that align with each perspective of the Balanced Scorecard. KPIs should be meaningful, quantifiable, and directly linked to the objectives. They should provide actionable insights into product performance and success.
After identifying KPIs, it is important to establish targets or benchmarks for each metric. Targets should be challenging yet attainable. They provide a reference point against which actual performance can be compared, enabling organizations to evaluate progress and identify areas for improvement.
Regular monitoring and analysis of the metrics are crucial for measuring product success. Organizations should establish a reporting and review process to track and assess performance against the defined objectives and targets. This can involve regular data collection, analysis, and reporting to key stakeholders.
Continuous monitoring enables organizations to identify trends, patterns, and areas of concern early on. It facilitates timely decision-making and intervention if needed. Regular reviews also create opportunities for learning, knowledge sharing, and improvement initiatives.
Adjustments and refinements to the metrics and targets may be necessary over time. As business conditions evolve and organizational strategies change, the Balanced Scorecard should be reviewed and updated accordingly. Flexibility and adaptability are essential to ensure the framework remains relevant and effective in measuring product success.
Conclusion
Using the Balanced Scorecard Framework is paramount for organizations seeking to measure product success accurately. By aligning strategic objectives with performance metrics, organizations can gain insights into various aspects of their products, customer experiences, internal processes, and growth potential.
As you navigate the realm of product success, consider adopting the Balanced Scorecard Framework as a practical tool. Assess your organization’s objectives, identify relevant metrics, and establish targets to measure and drive product success effectively. By embracing this framework, you can make informed decisions, enhance operational efficiency, foster innovation, and ultimately propel your products toward sustained success in today’s competitive landscape.
What metrics are you using to measure the success of your product? Let me know if the comments.


2 comments
First off I want to say fantastic blog! I had a quick question that I’d like to ask if you don’t mind.
I was curious to find out how you center yourself and clear
your thoughts before writing. I have had trouble clearing my mind in getting my thoughts out.
I truly do enjoy writing however it just seems like
the first 10 to 15 minutes are generally lost just trying
to figure out how to begin. Any suggestions or hints?
Thanks!
Hey people!!!!!
Good mood and good luck to everyone!!!!!
Comments are closed.